Technology
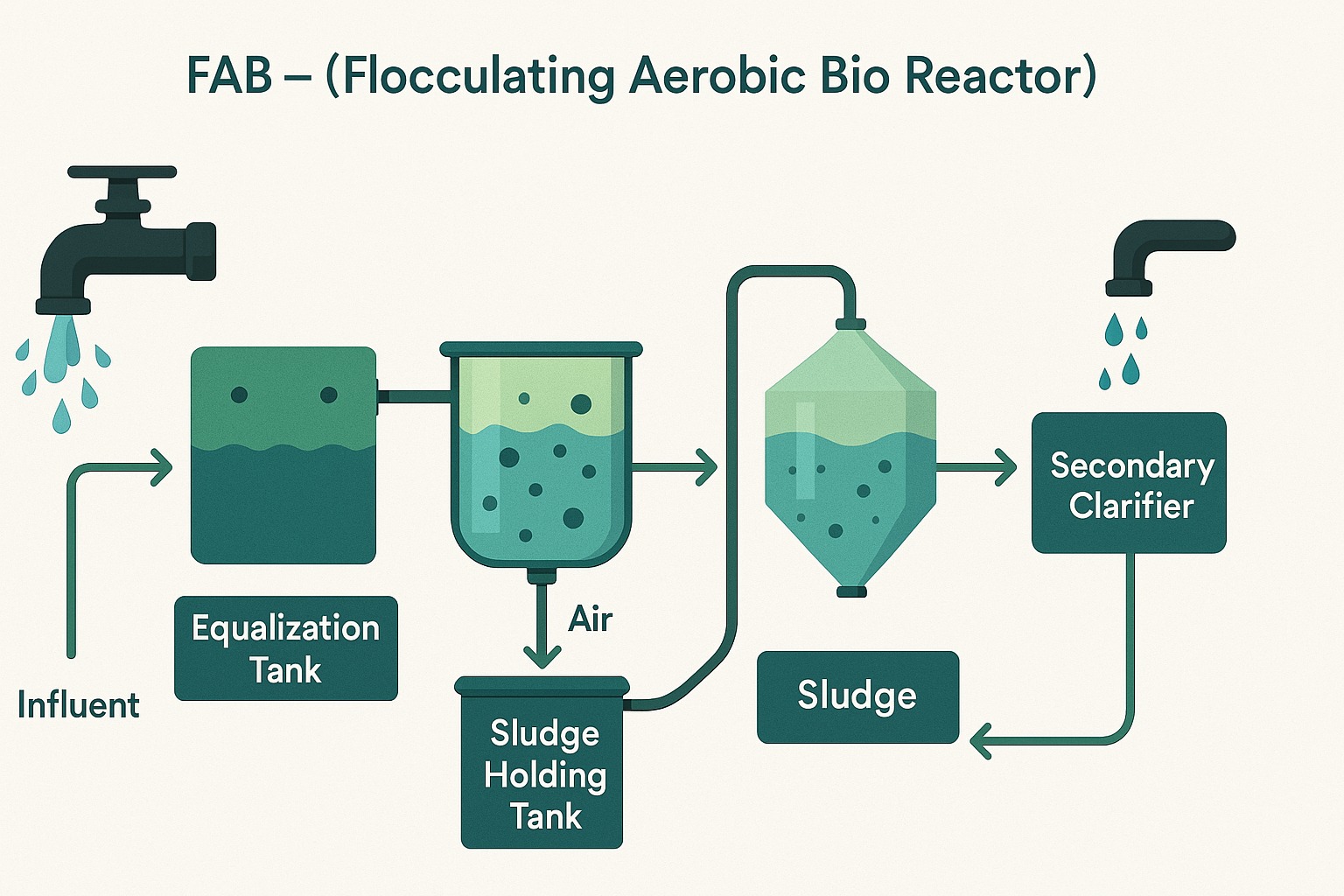
FAB – (Flocculating Aerobic Bio Reactor): FAB, or Flocculating Aerobic Bio Reactors, is a wastewater treatment technology that combines flocculation and aerobic biological treatment processes. It is designed to treat industrial or municipal wastewater effectively. In FAB systems, special chemicals called flocculants are used to encourage the aggregation of suspended particles in the wastewater into larger clumps or flocs. These flocs are then easier to remove during subsequent treatment steps.
The wastewater is subjected to aerobic biological treatment, where microorganisms break down organic contaminants in the presence of oxygen. This helps in further reducing the pollutant load in the wastewater.
FAB systems are known for their efficiency in removing pollutants and solids from wastewater, making them a valuable component in wastewater treatment plants. They are often used in scenarios where a high degree of pollutant removal is required to meet stringent water quality standards.
SAFF – (Submerged Aerobic Fixed Film): In a SAFF system, specially designed filter media is submerged in wastewater or water to facilitate the growth of beneficial microorganisms. These microorganisms help break down and remove organic pollutants and other contaminants from the water through biological processes. As air is introduced into the system, it provides oxygen to the microorganisms, allowing them to efficiently degrade the pollutants.
SAFF systems are known for their effectiveness in treating both domestic and industrial wastewater and are often used as part of a larger wastewater treatment plant. They are particularly useful in scenarios where high-quality effluent is required, and they contribute to improving water quality before discharge or reuse.

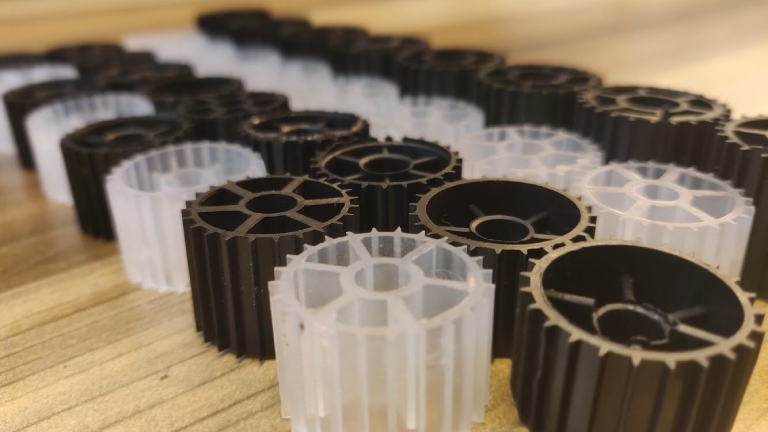
MBBR – (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor): MBBR stands for Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor, which is a widely used wastewater treatment technology. It’s a biological treatment process that combines the principles of activated sludge and biofilm processes to treat wastewater effectively.
In an MBBR system, small plastic carriers with a large surface area are suspended in a wastewater tank. These carriers provide a substrate for beneficial microorganisms to attach and grow as a biofilm. As wastewater flows through the reactor, microorganisms on the carriers consume and biologically break down organic matter and other pollutants in the water.
One of the key advantages of MBBR is its flexibility and adaptability to various wastewater treatment applications. It’s often used for both municipal and industrial wastewater treatment due to its high treatment efficiency, compact design, and ease of retrofitting into existing treatment plants. MBBR systems can be employed for both biological oxygen demand (BOD) and ammonia removal, making them versatile in addressing different wastewater treatment needs.

SBR – (Sequence Batch Reactor): SBR stands for Sequencing Batch Reactor, which is a wastewater treatment process that treats sewage and industrial wastewater. In an SBR system, wastewater is treated in batches, going through a series of phases including filling, aeration, settling, and decanting. This process helps remove contaminants and pollutants from the wastewater before it is discharged or further treated. SBRs are known for their flexibility and efficiency in treating different types of wastewater.
MBR – (Membrane Bio Reactor): MBR stands for Membrane Bioreactor, which is another advanced wastewater treatment technology. In MBR systems, biological processes (similar to those in traditional wastewater treatment plants) are combined with membrane filtration. The key component of MBR is the use of semi-permeable membranes to separate solids and microorganisms from the treated water.
The advantages of MBR include high-quality effluent, a smaller footprint compared to conventional treatment plants, and the ability to remove a wide range of contaminants effectively. MBR systems are commonly used in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment applications.
.




